
Scroll through time.
Learn your history.

The Angels are concerned about the new creation.
Allah creates the first human being, Adam 


Adam 
Allah creates a companion for Adam 
Qabil harbours jealousy towards his brother Habil. A sacrifice is sought to solve a matter but intensifies when his own sacrifice is rejected while Habil's is accepted.

Qabil commits the first murder among mankind by killing his brother Habil. After the act, Qabil experiences feelings of regret and remorse but is uncertain about what steps to take next.
Adam’s 


Prophet Sheeth was the third son of Prophet Adam and Hawwa (Eve), born after the death of his brother Habil (Abel).

The name "Sheeth" means "Gift from Allah" because he was born after the tragic loss of Habil.

His father taught him the hours of the days and night and the act of worship to be performed in those hours.

Sheeth was chosen by Allah to lead the descendants of Adam. He was known for his piety, righteousness, and devotion to Allah.

Allah revealed fifty scrolls (Suhuf) to Sheeth, containing guidance and laws for his people. He received divine guidance to lead his people and maintain the monotheistic teachings passed down from Adam 

Prophet Idris 




Allah describes Idris 

Idris 

Driven by a powerful desire to increase his reward, Idris 

Allah counted Idris 
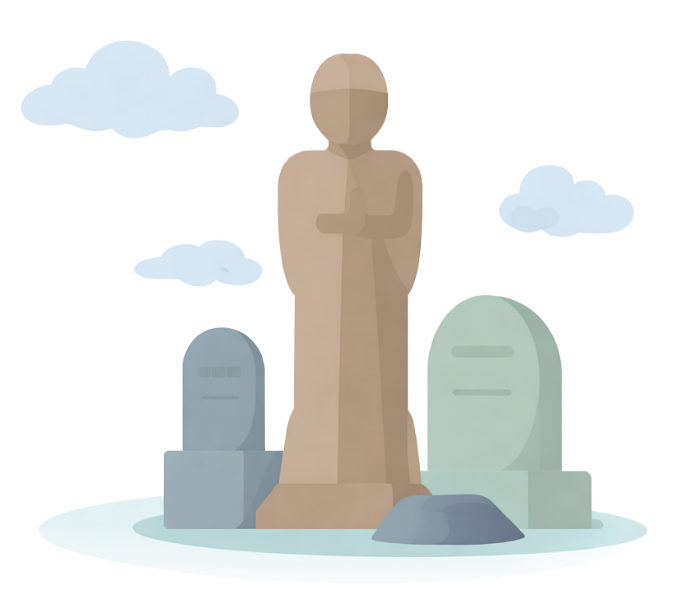
The generation between Adam and Nuh adhered to the belief in the oneness of Allah following the Sharee’ah. However, over time, deviation from monotheism emerged and the spread of shirk accelerated. Influenced by shaytaan’s whispers and deception, shaytan began corrupting the people’s belief by encouraging them to visit the graves of righteous individuals, constructing statues in remembrance of them and, subsequently worshiping them alongside Allah.

Nuh, the first messenger sent to mankind has been commanded by Allah to call the people back to righteousness. Nuh, upon steadfastness and resilience, calls his people for 950 years employing various methods to his people to abandon shirk and return back to Tawheed.
Despite his sincere advice and warning, Nuh (AS) was faced with severe opposition from his people.

As the situation with his people grew increasingly dire, Allah revealed to Prophet Nuh that none among his people who hadn’t believed now, would not be saved.
In response to this revelation, Nuh fervently supplicated to Allah, day and night seeking his aid and assistance.

Upon granting Nuh's request, Allah ordered Nuh (AS) to construct an Ark and to embark upon it with those who believed and with each kind of animal, male and female.
While constructing the Ark, Nuh was met with mockery and ridicule from his people; however, he still remained steadfast carrying out the commands of Allah.
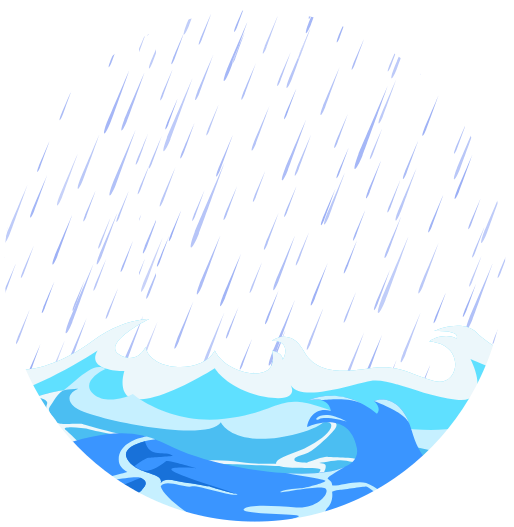

Allah sent his divine punishment upon the people of Nuh (AS). In the face of the impending flood, the people of Nuh sought to flee for safety but as the floodwater gushed forth from the earth, and poured from the heavens, the rain engulfed the land and submerged everything in its path.
Allah’s decree was fulfilled and the disbelievers from the people of Nuh were destroyed. There were no survivors that day.
Despites Nuh's earnest efforts calling his people back to Tawheed, among those who were destroyed with the disbelievers were Nuh's wife and his son.
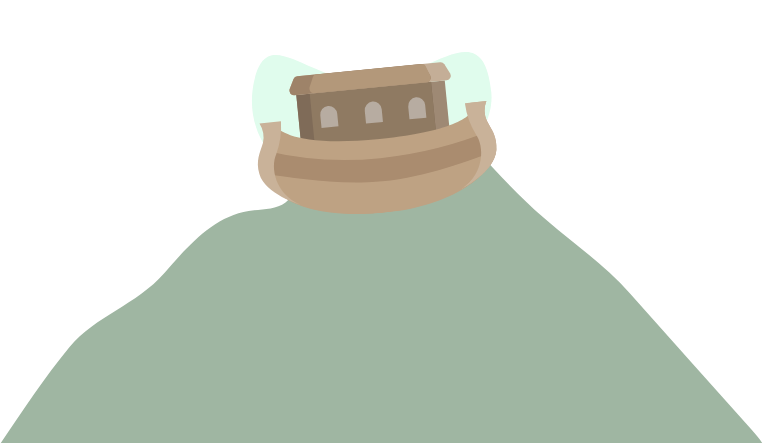

After the flood subsided and Nuh and those who were on the Ark with him were saved, Allah caused the idols to be buried.
Nuh continued to advise and warn his people on being upon the obedience of Allah and to be weary of the trials of this world.
The Ad tribe lived in Yemen in the desert in a region between Hadramout and Oman. They were renowned for their great physical stature and the grand buildings they constructed.
Despite their power, Ad were a disbelieving people; they were unjust and worshipped idols.

Prophet Hud 

 APPEAL TO HIS PEOPLE
APPEAL TO HIS PEOPLE
Prophet Hud 

 EXPLAINS THE DAY OF JUDGEMENT
EXPLAINS THE DAY OF JUDGEMENT
Prophet Hud 
The people of Ad remained stubborn in their disbelief, mocking Prophet Hud’s


 WARNS HIS PEOPLE
WARNS HIS PEOPLE
Hud continued to warn his people of Allah’s impending punishment, urging them to seek forgiveness and repent.
However, the people of Ad remained defiant, insisting that their wealth and towering structures would protect
them. They refused to believe that Hud


Allah sent a severe drought and, later, a violent windstorm destroyed the Ad. The storm, which lasted eight
days and seven nights, reducing everything to ruins. Only Prophet Hud


After the people of Ad were destroyed, the tribe of Thamud rose to power and wealth. However, as they grew richer, they also became more corrupt. They built impressive buildings and carved homes from the hills, but their moral values declined, and evil rulers took control of the land.


Allah sent Prophet Salih 

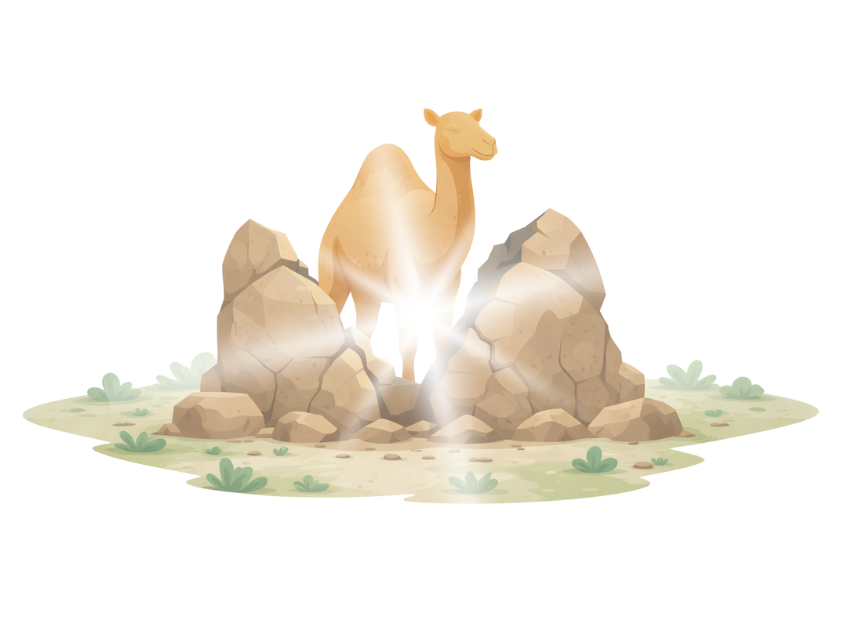
The people of Thamud asked Salih 


Salih 
Influenced by their leaders and tempted by rewards, several men killed the camel. They celebrated their act
and mocked Salih. Prophet Sailh


Three days after the camel was killed, Allah sent a punishment of a Blast from the sky and a violent earthquake. The entire tribe of Thamud was destroyed, except for those who had believed and left.

Prophet Ibrahim 

Ibrahim 

Upon receiving divine guidance, Ibrahim 

Upon receiving divine guidance, Ibrahim 

In a bold act of defiance, Ibrahim 

After breaking the idols, Ibrahim was sentenced to be burned alive by his people. However, Allah miraculously saved him by making the fire cool and safe for him. This event is a powerful example of how Allah rewards and protects those who have complete trust in Him, even in the most perilous situations.

After facing relentless opposition and hostility from his people, Ibrahim migrated to seek a land where he could worship Allah freely. His hijrah (migration) exemplifies the concept of leaving one’s home, comfort, and security for the sake of Allah, highlighting the sacrifices required in the path of faith.

Ibrahim’s 

Ibrahim’s 

Ibrahim 

Ibrahim, along with his son Ismaeel, was chosen by Allah to build the Ka'bah in Makkah, the first house of worship dedicated to the oneness of Allah. The construction of the Ka'bah solidified the foundation of monotheism, and to this day, it remains the focal point of Muslim worship worldwide. This event underscores the lasting impact of Ibrahim’s mission.

Ibrahim

The relationship between Prophet Ibrahim and other prophets, such as Nuh (Noah) before him and his own sons, Ismaeel and Ishaq, highlights the continuity of the message of monotheism. His influence extended to the prophets who followed, with his teachings deeply impacting their missions and the prophetic tradition.

Ibrahim’s life is a model of Tawakkul (trust in Allah), from leaving his homeland, facing the fire, to being tested with the sacrifice of his son. His constant reliance on Allah’s wisdom and mercy, even in the most challenging circumstances, offers profound lessons in how to maintain faith and trust in Allah’s plan.

Ibrahim’s 


Prophet Lut was the nephew of Prophet Ibrahim. He was sent by Allaah to call his people to worship Allaah alone and obedience and away from polytheism and immorality. From the sins that his people often indulged in was the sin of homosexuality.

The three angels (Jibreel, Mika’eel, and Israfeel) visited Prophet Ibrahim and during this visit, they informed him that they were sent by Allaah to punish the people of Lut due to their evil deeds. At the same time, Prophet Lut was determined to call them to the straight path but his people mocked him and thought about expelling him from their land. This all resulted in Lut supplicating against his own people after they asked to be punished out of arrogance.


When Prophet Ibrahim heard the angels saying they would punish the people of Lut, he tried to intercede on their behalf because he hoped that they would eventually accept the call. However, Allaah informd us that this wouldn’t happen as they were stubborn and turned away every time guidance came to them.


The angels then went to Prophet Lut’s house, appearing in the forms of handsome young men as a test for his people. Upon this, Lut took them in secretly since his people had tried to forbid him from that. His wife, however, went and told them what Prophet Lut was doing which caused them to race to his house.

When they arrived, Lut admonished his people again and encouraged them to marry women and cease from their immoral act. He then testified that they were an evil people who didn’t have a single pious man amongst them. After hearing this, the angels began to carry out the punishment against the people.

The towns of Sodom in Palestine were turned completely upside down and Allaah rained upon them stones of baked clay. Prophet Lut’s wife was also punished as she was a disbeliever and acted as a spy against her husband. She was not; however, a lewd person as the wives of the prophets cannot fall into such a thing.

Prophet Ismail 





Prophet Ismail 

Prophet Ibrahim 


Prophet Ismail 


Prophet Ismail 


Yaqoub 


Yaqoub 

Prophet Yaqoub 

After years of grief and trust in Allah, Yaqoub 

Even after his death, Yaqoub 


Yusuf 


Out of envy, Yusuf’s 


A passing caravan rescued Yusuf 

Zulaikha, the wife of Al-Aziz, attempted to seduce Yusuf 

In prison, Yusuf 


Years later, the king had a perplexing dream that no one could explain, prompting the freed prisoner to remember Yusuf 



Yusuf’s 


After failing to secure Binyamin’s release, the brothers returned to Yaqoub 




After suffering great trials, Yusuf 


At the height of his success, Yusuf 

Yaqoub 


Understanding the historical background of Misr is key to understanding the story of Musa and who the real so-called Pharaohs were. Understand the mistakes in western history, and the claims of the modern day Jews.

Firawn the tyrant ruler slaughtered the children of Bani Israel. Prophet Musa 

Musa 

Musa 


The burning bush marked the beginning of Musa’s divine mission to challenge the tyranny of Firawn and free Bani Israel. Allah supported Musa with miracles and taught reliance upon Him, the power of dua, and trust in Allah during hardship.

Musa 


Musa 

Pharaoh continued to oppress Bani Israel and refused to release them. Musa led them out by night, but Pharaoh pursued them. Allah answered Musa’s supplication and destroyed Pharaoh when the sea parted for Bani Israel and drowned Pharaoh and his army.

Musa 

Musa 

Musa 

Musa 

Dawud 

Dawud 

During the conflict between the Israelites and the Philistines, Jalut challenged Talut, the king at the time, to fight him. Talut announced this challenge to the people, but only Dawud 

Dawud 
Dawud 

Dawud 

The Zaboor was revealed to Dawud 

Dawud 

Allah guided Dawud 

Dawud 


Prophet Sulaiman 

Allah blessed Sulaiman 

Prophet Sulaiman 

One of the famous stories about Sulaiman 

The hoopoe bird played a key role in delivering the news of a distant kingdom ruled by the Queen of Sheba. Upon hearing this, Sulaiman 

Allah gave Sulaiman 

The Queen of Sheba, known as Bilqis, ruled over a prosperous kingdom that worshipped the sun. After receiving Sulaiman’s invitation and witnessing signs of Allah’s power, she submitted to Allah and embraced Islam.

By Allah’s will, the throne of the Queen of Sheba was brought to Sulaiman’s 

Sulaiman’s 

Despite his immense power, Sulaiman 

Sulaiman 

Sulaiman’s 
 COMPANIONS OF THE PROPHET ﷺ
COMPANIONS OF THE PROPHET ﷺ